Hadoop集群(第9期)_MapReduce初级案例(2)。
3、平均成绩
“平均成绩”主要目的还是在重温经典“WordCount”例子,可以说是在基础上的微变化版,该实例主要就是实现一个计算学生平均成绩的例子。
3.1 实例描述
对输入文件中数据进行就算学生平均成绩。输入文件中的每行内容均为一个学生的姓名和他相应的成绩,如果有多门学科,则每门学科为一个文件。要求在输出中每行有两个间隔的数据,其中,第一个代表学生的姓名,第二个代表其平均成绩。
样本输入:
1)math:
张三 88
李四 99
王五 66
赵六 77
2)china:
张三 78
李四 89
王五 96
赵六 67
3)english:
张三 80
李四 82
王五 84
赵六 86
样本输出:
张三 82
李四 90
王五 82
赵六 76
3.2 设计思路
计算学生平均成绩是一个仿”WordCount”例子,用来重温一下开发MapReduce程序的流程。程序包括两部分的内容:Map部分和Reduce部分,分别实现了map和reduce的功能。
Map处理的是一个纯文本文件, 文件中存放的数据时每一行表示一个学生的姓名和他相应一科成绩。Mapper处理的数据是由InputFormat分解过的数据集,其中 InputFormat的作用是将数据集切割成小数据集InputSplit,每一个InputSlit将由一个Mapper负责处理。此 外,InputFormat中还提供了一个RecordReader的实现,并将一个InputSplit解析成<key,value>对提 供给了map函数。InputFormat的默认值是TextInputFormat,它针对文本文件,按行将文本切割成InputSlit,并用 LineRecordReader将InputSplit解析成<key,value>对,key是行在文本中的位置,value是文件中的 一行。
Map的结果会通过partion分发到Reducer,Reducer做完Reduce操作后,将通过以格式OutputFormat输出。
Mapper最终处理的结果对<key,value>,会送到Reducer中进行合并,合并的时候,有相同key的键/值对则送到同一个 Reducer上。Reducer是所有用户定制Reducer类地基础,它的输入是key和这个key对应的所有value的一个迭代器,同时还有 Reducer的上下文。Reduce的结果由Reducer.Context的write方法输出到文件中。
3.3 程序代码
程序代码如下所示:
package com.hebut.mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class Score {
public static class Map extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
// 实现map函数
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 将输入的纯文本文件的数据转化成String
String line = value.toString();
// 将输入的数据首先按行进行分割
StringTokenizer tokenizerArticle = new StringTokenizer(line,”\n”);
// 分别对每一行进行处理
while (tokenizerArticle.hasMoreElements()) {
// 每行按空格划分
StringTokenizer tokenizerLine = newStringTokenizer(tokenizerArticle.nextToken());
String strName = tokenizerLine.nextToken();// 学生姓名部分
String strScore = tokenizerLine.nextToken();// 成绩部分
Text name = new Text(strName);
int scoreInt = Integer.parseInt(strScore);
// 输出姓名和成绩
context.write(name, newIntWritable(scoreInt));
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
// 实现reduce函数
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
Iterator<IntWritable> iterator = values.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
sum += iterator.next().get();// 计算总分
count++;// 统计总的科目数
}
int average = (int) sum / count;// 计算平均成绩
context.write(key, new IntWritable(average));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throwsException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 这句话很关键
conf.set(“mapred.job.tracker”,”192.168.1.2:9001″);
String[] ioArgs = new String[] { ”score_in”,”score_out” };
String[] otherArgs = newGenericOptionsParser(conf, ioArgs).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println(“Usage: Score Average <in> <out>”);
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, ”Score Average”);
job.setJarByClass(Score.class);
// 设置Map、Combine和Reduce处理类
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
// 设置输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 将输入的数据集分割成小数据块splites,提供一个RecordReder的实现
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// 提供一个RecordWriter的实现,负责数据输出
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 设置输入和输出目录
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, newPath(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, newPath(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
3.4 代码结果
1)准备测试数据
通过Eclipse下面的”DFS Locations”在”/user/hadoop”目录下创建输入文件”score_in”文件夹(备注:”score_out”不需要创建。)如图3.4-1所示,已经成功创建。
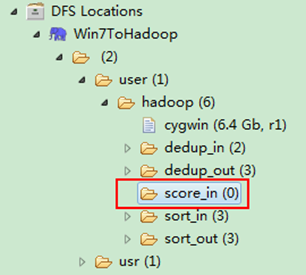
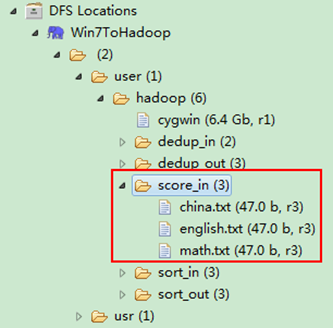
图3.4-1 创建”score_in” 图3.4.2 上传三门分数
然后在本地建立三个txt文件,通过Eclipse上传到”/user/hadoop/score_in”文件夹中,三个txt文件的内容如”实例描述”那三个文件一样。如图3.4-2所示,成功上传之后。
备注:文本文件的编码为”UTF-8“,默认为”ANSI“,可以另存为时选择,不然中文会出现乱码。
从SecureCRT远处查看”Master.Hadoop”的也能证实我们上传的三个文件。

查看三个文件的内容如图3.4-3所示:
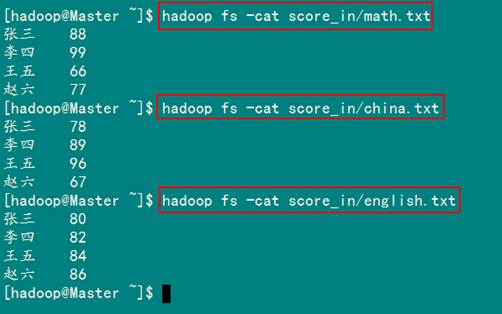
图3.4.3 三门成绩的内容
2)查看运行结果
这时我们右击Eclipse 的”DFS Locations”中”/user/hadoop”文件夹进行刷新,这时会发现多出一个”score_out”文件夹,且里面有3个文件,然后打开双 其”part-r-00000″文件,会在Eclipse中间把内容显示出来。如图3.4-4所示。
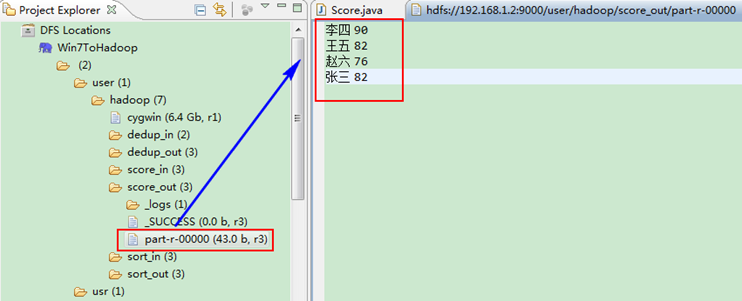
图3.4-4 运行结果
4、单表关联
前面的实例都是在数据上进行一些简单的处理,为进一步的操作打基础。”单表关联“这个实例要求从给出的数据中寻找所关心的数据,它是对原始数据所包含信息的挖掘。下面进入这个实例。
4.1 实例描述
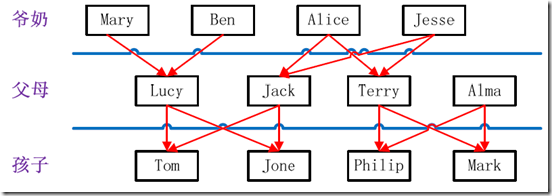
实例中给出child-parent(孩子——父母)表,要求输出grandchild-grandparent(孙子——爷奶)表。
样例输入如下所示。
file:
child parent
Tom Lucy
Tom Jack
Jone Lucy
Jone Jack
Lucy Mary
Lucy Ben
Jack Alice
Jack Jesse
Terry Alice
Terry Jesse
Philip Terry
Philip Alma
Mark Terry
Mark Alma
家族树状关系谱:
图4.2-1 家族谱
样例输出如下所示。
file:
grandchild grandparent
Tom Alice
Tom Jesse
Jone Alice
Jone Jesse
Tom Mary
Tom Ben
Jone Mary
Jone Ben
Philip Alice
Philip Jesse
Mark Alice
Mark Jesse
4.2 设计思路
分析这个实例,显然需要进行单表连接,连接的是左表的parent列和右表的child列,且左表和右表是同一个表。
连接结果中除去连接的两列就是所需要的结果——”grandchild–grandparent”表。要用MapReduce解决这个实例,首先应该考虑如何实现表的自连接;其次就是连接列的设置;最后是结果的整理。
考虑到MapReduce的shuffle过程会将相同的key会连接在一起,所以可以将map结果的key设置成待连接的列,然后列中相同的值就自然会连接在一起了。再与最开始的分析联系起来:
要连接的是左表的parent列和右表的child列,且左表和右表是同一个表,所以在map阶段将读入数据分割成child和parent之后,会将parent设置成key,child设置成value进行输出,并作为左表;再将同一对child和parent中的child设置成key,parent设置成value进行输出,作为右表。为了区分输出中的左右表,需要在输出的value中再加上左右表的信息,比如在value的String最开始处加上字符1表示左表,加上字符2表示右表。这样在map的结果中就形成了左表和右表,然后在shuffle过程中完成连接。reduce接收到连接的结果,其中每个key的value-list就包含了”grandchild–grandparent”关系。取出每个key的value-list进行解析,将左表中的child放入一个数组,右表中的parent放入一个数组,然后对两个数组求笛卡尔积就是最后的结果了。
4.3 程序代码
程序代码如下所示。
package com.hebut.mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class STjoin {
public static int time = 0;
/*
* map将输出分割child和parent,然后正序输出一次作为右表,
* 反序输出一次作为左表,需要注意的是在输出的value中必须
* 加上左右表的区别标识。
*/
public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
// 实现map函数
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String childname = new String();// 孩子名称
String parentname = new String();// 父母名称
String relationtype = new String();// 左右表标识
// 输入的一行预处理文本
StringTokenizer itr=newStringTokenizer(value.toString());
String[] values=new String[2];
int i=0;
while(itr.hasMoreTokens()){
values[i]=itr.nextToken();
i++;
}
if (values[0].compareTo(“child”) != 0) {
childname = values[0];
parentname = values[1];
// 输出左表
relationtype = ”1″;
context.write(new Text(values[1]), newText(relationtype +
“+”+ childname + ”+” + parentname));
// 输出右表
relationtype = ”2″;
context.write(new Text(values[0]), newText(relationtype +
“+”+ childname + ”+” + parentname));
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
// 实现reduce函数
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 输出表头
if (0 == time) {
context.write(new Text(“grandchild”), newText(“grandparent”));
time++;
}
int grandchildnum = 0;
String[] grandchild = new String[10];
int grandparentnum = 0;
String[] grandparent = new String[10];
Iterator ite = values.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
String record = ite.next().toString();
int len = record.length();
int i = 2;
if (0 == len) {
continue;
}
// 取得左右表标识
char relationtype = record.charAt(0);
// 定义孩子和父母变量
String childname = new String();
String parentname = new String();
// 获取value-list中value的child
while (record.charAt(i) != ’+') {
childname += record.charAt(i);
i++;
}
i = i + 1;
// 获取value-list中value的parent
while (i < len) {
parentname += record.charAt(i);
i++;
}
// 左表,取出child放入grandchildren
if (’1′ == relationtype) {
grandchild[grandchildnum] = childname;
grandchildnum++;
}
// 右表,取出parent放入grandparent
if (’2′ == relationtype) {
grandparent[grandparentnum] = parentname;
grandparentnum++;
}
}
// grandchild和grandparent数组求笛卡尔儿积
if (0 != grandchildnum && 0 != grandparentnum) {
for (int m = 0; m < grandchildnum; m++) {
for (int n = 0; n < grandparentnum; n++) {
// 输出结果
context.write(newText(grandchild[m]), new Text(grandparent[n]));
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throwsException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 这句话很关键
conf.set(“mapred.job.tracker”,”192.168.1.2:9001″);
String[] ioArgs = new String[] { ”STjoin_in”,”STjoin_out” };
String[] otherArgs = newGenericOptionsParser(conf, ioArgs).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println(“Usage: Single Table Join <in> <out>”);
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, ”Single Table Join”);
job.setJarByClass(STjoin.class);
// 设置Map和Reduce处理类
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
// 设置输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// 设置输入和输出目录
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, newPath(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, newPath(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
4.4 代码结果
1)准备测试数据
通过Eclipse下面的”DFS Locations”在”/user/hadoop”目录下创建输入文件”STjoin_in”文件夹(备注:”STjoin_out”不需要创建。)如图4.4-1所示,已经成功创建。
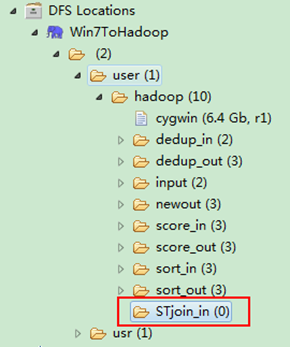
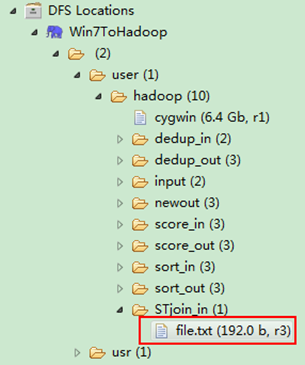
图4.4-1 创建”STjoin_in” 图4.4.2 上传”child-parent”表
然后在本地建立一个txt文件,通过Eclipse上传到”/user/hadoop/STjoin_in”文件夹中,一个txt文件的内容如”实例描述”那个文件一样。如图4.4-2所示,成功上传之后。
从SecureCRT远处查看”Master.Hadoop”的也能证实我们上传的文件,显示其内容如图4.4-3所示:
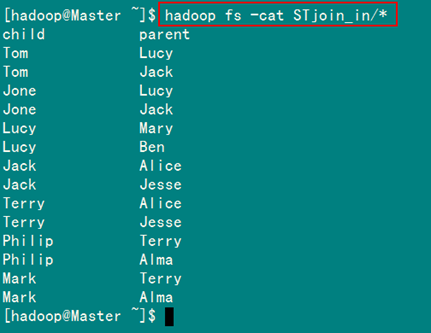
图4.4-3 表”child-parent”内容
2)运行详解
(1)Map处理:
map函数输出结果如下所示。
child parent àà 忽略此行
Tom Lucy àà <Lucy,1+Tom+Lucy>
<Tom,2+Tom+Lucy >
Tom Jack àà <Jack,1+Tom+Jack>
<Tom,2+Tom+Jack>
Jone Lucy àà <Lucy,1+Jone+Lucy>
<Jone,2+Jone+Lucy>
Jone Jack àà <Jack,1+Jone+Jack>
<Jone,2+Jone+Jack>
Lucy Mary àà <Mary,1+Lucy+Mary>
<Lucy,2+Lucy+Mary>
Lucy Ben àà <Ben,1+Lucy+Ben>
<Lucy,2+Lucy+Ben>
Jack Alice àà <Alice,1+Jack+Alice>
<Jack,2+Jack+Alice>
Jack Jesse àà <Jesse,1+Jack+Jesse>
<Jack,2+Jack+Jesse>
Terry Alice àà <Alice,1+Terry+Alice>
<Terry,2+Terry+Alice>
Terry Jesse àà <Jesse,1+Terry+Jesse>
<Terry,2+Terry+Jesse>
Philip Terry àà <Terry,1+Philip+Terry>
<Philip,2+Philip+Terry>
Philip Alma àà <Alma,1+Philip+Alma>
<Philip,2+Philip+Alma>
Mark Terry àà <Terry,1+Mark+Terry>
<Mark,2+Mark+Terry>
Mark Alma àà <Alma,1+Mark+Alma>
<Mark,2+Mark+Alma>
(2)Shuffle处理
在shuffle过程中完成连接。
| map函数输出 | 排序结果 | shuffle连接 |
| <Lucy,1+Tom+Lucy>
<Tom,2+Tom+Lucy> <Jack,1+Tom+Jack> <Tom,2+Tom+Jack> <Lucy,1+Jone+Lucy> <Jone,2+Jone+Lucy> <Jack,1+Jone+Jack> <Jone,2+Jone+Jack> <Mary,1+Lucy+Mary> <Lucy,2+Lucy+Mary> <Ben,1+Lucy+Ben> <Lucy,2+Lucy+Ben> <Alice,1+Jack+Alice> <Jack,2+Jack+Alice> <Jesse,1+Jack+Jesse> <Jack,2+Jack+Jesse> <Alice,1+Terry+Alice> <Terry,2+Terry+Alice> <Jesse,1+Terry+Jesse> <Terry,2+Terry+Jesse> <Terry,1+Philip+Terry> <Philip,2+Philip+Terry> <Alma,1+Philip+Alma> <Philip,2+Philip+Alma> <Terry,1+Mark+Terry> <Mark,2+Mark+Terry> <Alma,1+Mark+Alma> <Mark,2+Mark+Alma> |
<Alice,1+Jack+Alice>
<Alice,1+Terry+Alice> <Alma,1+Philip+Alma> <Alma,1+Mark+Alma> <Ben,1+Lucy+Ben> <Jack,1+Tom+Jack> <Jack,1+Jone+Jack> <Jack,2+Jack+Alice> <Jack,2+Jack+Jesse> <Jesse,1+Jack+Jesse> <Jesse,1+Terry+Jesse> <Jone,2+Jone+Lucy> <Jone,2+Jone+Jack> <Lucy,1+Tom+Lucy> <Lucy,1+Jone+Lucy> <Lucy,2+Lucy+Mary> <Lucy,2+Lucy+Ben> <Mary,1+Lucy+Mary> <Mark,2+Mark+Terry> <Mark,2+Mark+Alma> <Philip,2+Philip+Terry> <Philip,2+Philip+Alma> <Terry,2+Terry+Alice> <Terry,2+Terry+Jesse> <Terry,1+Philip+Terry> <Terry,1+Mark+Terry> <Tom,2+Tom+Lucy> <Tom,2+Tom+Jack> |
<Alice,1+Jack+Alice,
1+Terry+Alice , 1+Philip+Alma, 1+Mark+Alma > <Ben,1+Lucy+Ben> <Jack,1+Tom+Jack, 1+Jone+Jack, 2+Jack+Alice, 2+Jack+Jesse > <Jesse,1+Jack+Jesse, 1+Terry+Jesse > <Jone,2+Jone+Lucy, 2+Jone+Jack> <Lucy,1+Tom+Lucy, 1+Jone+Lucy, 2+Lucy+Mary, 2+Lucy+Ben> <Mary,1+Lucy+Mary, 2+Mark+Terry, 2+Mark+Alma> <Philip,2+Philip+Terry, 2+Philip+Alma> <Terry,2+Terry+Alice, 2+Terry+Jesse, 1+Philip+Terry, 1+Mark+Terry> <Tom,2+Tom+Lucy, 2+Tom+Jack> |
(3)Reduce处理
首先由语句”0 != grandchildnum && 0 != grandparentnum“得知,只要在”value-list”中没有左表或者右表,则不会做处理,可以根据这条规则去除无效的shuffle连接。
| 无效的shuffle连接 | 有效的shuffle连接 |
| <Alice,1+Jack+Alice,
1+Terry+Alice , 1+Philip+Alma, 1+Mark+Alma > <Ben,1+Lucy+Ben> <Jesse,1+Jack+Jesse, 1+Terry+Jesse > <Jone,2+Jone+Lucy, 2+Jone+Jack> <Mary,1+Lucy+Mary, 2+Mark+Terry, 2+Mark+Alma> <Philip,2+Philip+Terry, 2+Philip+Alma> <Tom,2+Tom+Lucy, 2+Tom+Jack> |
<Jack,1+Tom+Jack,
1+Jone+Jack, 2+Jack+Alice, 2+Jack+Jesse > <Lucy,1+Tom+Lucy, 1+Jone+Lucy, 2+Lucy+Mary, 2+Lucy+Ben> <Terry,2+Terry+Alice, 2+Terry+Jesse, 1+Philip+Terry, 1+Mark+Terry> |
然后根据下面语句进一步对有效的shuffle连接做处理。
// 左表,取出child放入grandchildren
if (’1′ == relationtype) {
grandchild[grandchildnum] = childname;
grandchildnum++;
}
// 右表,取出parent放入grandparent
if (’2′ == relationtype) {
grandparent[grandparentnum] = parentname;
grandparentnum++;
}
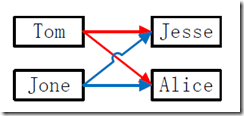
针对一条数据进行分析:
<Jack,1+Tom+Jack,
1+Jone+Jack,
2+Jack+Alice,
2+Jack+Jesse >
分析结果:左表用”字符1“表示,右表用”字符2“表示,上面的<key,value-list>中的”key“表示左表与右表的连接键。而”value-list“表示以”key”连接的左表与右表的相关数据。
根据上面针对左表与右表不同的处理规则,取得两个数组的数据如下所示:
| grandchild | Tom、Jone(grandchild[grandchildnum] = childname;) |
| grandparent | Alice、Jesse(grandparent[grandparentnum] = parentname;) |
然后根据下面语句进行处理。
for (int m = 0; m < grandchildnum; m++) {
for (int n = 0; n < grandparentnum; n++) {
context.write(new Text(grandchild[m]), new Text(grandparent[n]));
}
}
处理结果如下面所示:
| Tom Jesse
Tom Alice Jone Jesse Jone Alice |
其他的有效shuffle连接处理都是如此。
3)查看运行结果
这时我们右击Eclipse 的”DFS Locations”中”/user/hadoop”文件夹进行刷新,这时会发现多出一个”STjoin_out”文件夹,且里面有3个文件,然后打开双 其”part-r-00000″文件,会在Eclipse中间把内容显示出来。如图4.4-4所示。
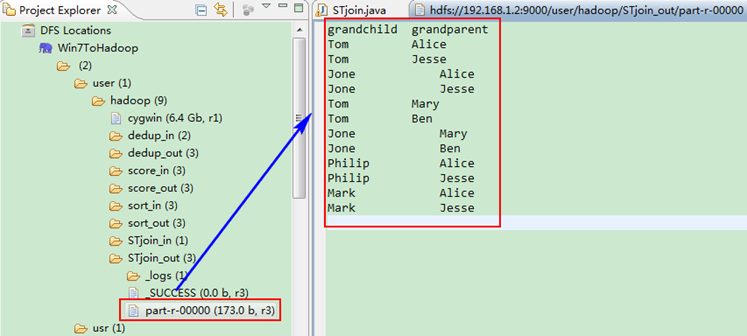
图4.4-4 运行结果