AOP开发之开发Spring AOP程序
这是漫谈AOP系列的第三篇,前两篇请看
我们还是以《漫谈AOP开发之初探AOP及AspectJ的用法》中的例子为例继续,我们在Eclipse中创建一个新的工程,导入UserService、BookService两个类,并配置Spring的Bean:
<bean id="us" class="com.mybry.aop.service.UserService"/><bean id="bs" class="com.mybry.aop.service.BookService"/>写一个增强处理类(Advice):
package com.mybry.aop.aspect;public class AuthAspect { public void auth() { System.out.println("====执行权限检查的方法===="); }}在前面的文章我们说过了,Spring AOP框架是在运行阶段动态生成AOP代理(在内存中动态地生成AOP代理类),以实现对目标对象的增强。它不需要特殊的编译器。所以不需要想AspectJ一样需要使用aspect声明类,这里直接用class即可。
接下来我们就在Spring中配置这个类:
<bean id=”authAspect” class=”com.mybry.aop.aspect.AuthAspect”/>
但此时Spring并知道这个类要作为Aspect使用的,这样依然只是一个普通的bean。还不知道要当肉来使用。这时候我们需要到如一个的明白空间AOP:
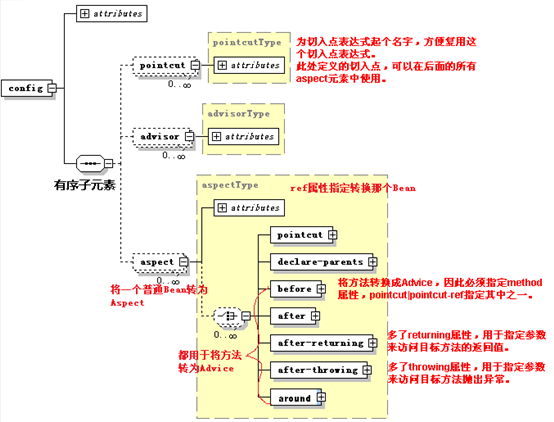
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd" >所有有关AOP的配置,都放在aop:config元素中:
<aop:config> <!-- 将authAspect转换为Aspect 指定在执行com.mybry.aop.service包下任意类、返回值不限的任意方法之前,织入auth方法。 --> <aop:aspect ref="authAspect"> <aop:before method="auth" pointcut="execution(* com.mybry.aop.service.*.*(..))"/> </aop:aspect></aop:config>AOP配置图:
注意,我们需要增加如下几个包:aopalliance、AspectJ、cglib。
运行上面的程序结果:
1、Spring支持的Advice
对于Advice而言,Spring一共支持5种Advice:
- Before: 在方法执行之前。
- AfterReturning: 只有成功返回后,才会织入该Advice
- AfterThrowing: 只有抛出异常后,才会织入该Advice
- After: 不管是抛出异常后,还是成功返回,都会织入该Advice
- Around: 在目标方法执行之前、之后,都织入该Advice。
2、AOP编程步骤总结
(1) 写普通类,将打算作为Aspect用,并将该类配置在Spring容器中。
(2) 用aop:aspect将普通Bean,转换为Aspect, 需要指定ref属性,该属性指定将哪个Bean转换为Aspect。
(3) 在aop:aspect元素中配置:
- aop:before.
- aop:after-returning. 额外可指定returning,用于访问目标方法的返回值。该属性指定的参数值,还可用于对目标方法的返回值类型进行限制。如果不想对目标方法返回值类型进行限制,只要声明该参数类型为Object即可。
- aop:after-throwing. 额外可指定throwing,用于访问目标方法的抛出的异常。该属性指定的参数值,还可用于对目标方法的抛出的异常类型进行限制。如果不想对目标方法抛出的异常类型类型进行限制,只要声明该参数类型为Exception即可
- aop:after 功能有点类似finally块,通常用于回收资源。
- aop:around, Advice方法,建议声明返回值,而且必须带一个ProceedingJoinPoint(AspectJ的API)类型的形参。
这5个元素,都可指定如下2个属性:
- method:指定把哪个方法转为Advice。
- pointcut|pointcut-ref:指定将Advice放到那些组件的哪些目标方法处。
3、Spring 的Advice的对比
| 动作 | Befor | AfterReturning | AfterThrowing | After | Around |
| 阻止方法执行 | 行(抛异常) | 不行 | 不行 | 不行 | 行 |
| 访问调用参数 | 行 | 行 | 行 | 行 | 行 |
| 修改调用参数 | 不行 | 不行 | 不行 | 不行 | 行 |
| 访问返回值 | 不行 | 行 | 不行 | 不行 | 行 |
| 修改返回值 | 不行 | 不行 | 不行 | 不行 | 行 |
4、访问调用参数
1)借助于Pointcut形参:只要为Advice方法增加一个JoinPoint形参,即可通过该形参来访 目标的参数。
XML:
<!-- args切入点表达式,用于限制目标方法必须有N个参数 --><aop:before method="auth" pointcut="execution(* com.mybry.aop.service.*.*(..)) and args(arg0, arg1) "/>JAVA:
public class AuthAspect{// 一旦在切入点表达式中使用args切入点表达式,即可在Advice方法中通过arg0、arg1来访问目标方法的调用参数public void auth(String arg0 , Object arg1){
System.out.println("模拟进行权限检查"); System.out.println("第1个参数为:" + arg0); System.out.println("第2个参数为:" + arg1);}}5、切入点表达式的写法简单介绍
execution([访问权限] [返回值类型] 包.类.方法(形参) [throws 异常]);
默认情况下,都可用*作为通配符。
形参列表支持2个通配符, ..代表任意个任意类型的参数; * 代表一个任意的参数。
(*, java.lang.String) 2个形参,且第二个形参必须是String
(.., java.lang.String) 1~N个形参,最后一个形参必须是String
target(类型) ——要求目标对象指定类型。
this(类型) ——要求AOP代理对象指定类型。
args(a,b) —— 要求目标方法必须有匹配的形参。
bean(beanid) —— 专门为用Spring的菜鸟准备的。 只为特定Bean的方法织入增强处理。原生AspectJ并不支持,只有用Spring才支持。
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="bean(us)" id="fkPc"/> <!-- 将authAspect转换为Aspect 指定在执行org.fkjava.aop.service包下任意类、返回值不限的任意方法之前,织入auth方法。 --> <aop:aspect ref="authAspect"> <!-- args切入点表达式,用于限制目标方法必须有N个参数 --> <aop:before method="auth" pointcut-ref="fkPc"/> </aop:aspect></aop:config>